 |
Saab 171940 |  |
| DIVE-BOMBER | Virtual Aircraft Museum / Sweden / Saab |
 |
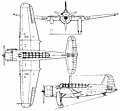
The Swedish company Svenska Aeroplan AB was established in 1937, combining AB Svenska Jarnvagsverkstaderna and Svenska Flygmotor AB, to build aircraft and aero-engines for the Swedish government and for export. Early licence production covered the Douglas 8A-1, similar to the US Army Air Corps' A-17; the Junkers Ju 86A twin-engined bomber; and the North American NA-16, from which was developed in the USA the AT-6 Texan. Saab's first original design was for a two-seat reconnaissance aircraft to meet an official requirement, but following the first flight of the Saab-17 prototype on 18 May 1940 the company made the proposal that its development as a bomber should be given consideration by the Flygvapen. Evaluation of the prototype led to the aircraft being developed for this role as well as for reconnaissance, and 325 were built. A cantilever mid-wing monoplane with retractable tail-wheel landing gear, the Saab-17 had its crew accommodated beneath a long continuous canopy. Powerplant varied, the B17A dive-bomber having the 794kW Swedish-built Pratt & Whitney R-1830-SC3G Twin Wasp radial, the B17B dive-bomber and similar S17B (equipped for the reconnaissance role) the 731kW Swedish-built Bristol Pegasus XXIV radial, and the B17C dive-bomber (which differed from the B17B only in its engine, the Piaggio P.XIbis). Included in the total production were 38 examples of the S17BS, a maritime patrol version of the B17B on twin floats. Many of the landplane versions were later given retractable ski landing gear for operation from snow-covered surfaces. Entering service with the Flygvapen in 1941, the Saab-17 was notable for the robust construction that has since been a feature of the company's designs, and the type remained in service until 1948. After World War II 47 were delivered to the Ethiopian air force. Saab 17 on YOUTUBE
|  COMPANY PROFILE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |

|


20
reply