|
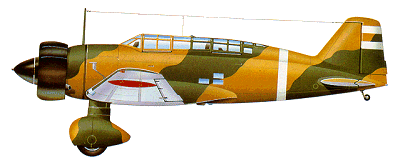
| In July 1935 the Imperial Japanese
Army drew up its specification for a
new two-seat reconnaissance aircraft,
and Mitsubishi responded with a cantilever
low-wing monoplane, the Mitsubishi
Ki-15. Service testing was completed
without difficulty and the type
was ordered into production under the
official designation Army Type 97
Command Reconnaissance Plane
Model 1. In May 1937, a year after the
first flight, delivery of production aircraft
to the army began.
Just before that, however, military
observers in the west should have
gained some premonition of Japan's
growing capability in aircraft design
when the second (civil) prototype was
used to establish a new record flight
time between Japan and England.
The army's Ki-15-I had been received
in time to make a significant
impact at the beginning of the war with
China, the type's high speed giving it
freedom of the skies until China introduced
the Soviet Polikarpov I-16.
However, plans had already been
made to upgrade performance of the
Ki-15-I, this being achieved by installing
the 671kW, smaller-diameter
Mitsubishi Ha-26-I engine, its incorporation
providing an opportunity
to overcome what had been the major
shortcoming of the type, a poor forward
field of view past the large-diameter
Nakajima engine. The improved
version entered production for
the army in September 1939 as the Ki-
15-II, but before that the Japanese
navy, impressed by the performance
of this aircraft, ordered 20 examples of
the Ki-15-II under the official designation
Navy Type 98 Reconnaissance
Plane Model 1, Mitsubishi designation
C5M1. The navy acquired subsequently
30 C5M2 aircraft that were generally
similar except for installation of the
more powerful 708kW Nakajima
Sakae (prosperity) 12 engine.
When production ended almost 500 of
all versions had been built, the majority
being in first-line service when the
Pacific war started. Given the Allied
codename 'Babs', the type was relegated
to second-line roles in early
1943, but many survived to be used in
kamikaze attacks at the war's end.
| MODEL | Ki-15-I |
| CREW | 2 |
| ENGINE | 1 x Army Type 99 Mod. 1, 640kW |
| WEIGHTS |
| Take-off weight | 2033-2300 kg | 4482 - 5071 lb |
| Empty weight | 1399 kg | 3084 lb |
| DIMENSIONS |
| Wingspan | 12.0 m | 39 ft 4 in |
| Length | 8.49 m | 28 ft 10 in |
| Height | 3.24 m | 11 ft 8 in |
| Wing area | 20.36 m2 | 219.15 sq ft |
| PERFORMANCE |
| Max. speed | 480 km/h | 298 mph |
| Cruise speed | 320 km/h | 199 mph |
| Ceiling | 11400 m | 37400 ft |
| Range | 2400 km | 1491 miles |
| ARMAMENT | 1 x 7.7mm machine-guns |
 | A three-view drawing (752 x 975) |
| ubaTaeCJ, e-mail, 21.02.2025 20:15 20 reply | | Henk, e-mail, 13.07.2011 11:33 It's a beauty, I am building a scale model reply |
| W.Groeneveld, e-mail, 18.05.2008 17:41 Were these C5M2's ever used from ships?,cuisers or carriers. reply |
|
Do you have any comments?
|
| 
COMPANY
PROFILE
All the World's Rotorcraft
|









20
reply