|
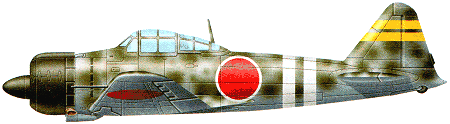
| The famous Mitsubishi A6M, popularly
known as the 'Zero', was the first carrierborne
fighter in the world capable
of outperforming any contemporary
land-based fighter it was likely to confront.
Because of inept Allied intelligence
it was able to achieve immediate
air superiority over the East Indies
and South East Asia from the day Japan
entered the war. Designed under the
leadership of Jiro Honkoshi in 1937 as a
replacement for the neat but obsolescent
A5M, the prototype A6M1 was
first flown on 1 April 1939 with a 582kW Mitsubishi Zuisei 13 radial;
production A6M2 fighters with
two wing-mounted 20mm guns and
two nose-mounted 7.7mm guns were fitted with the 708kW Nakajima Sakae 12 radial, and
it was with this version that the
Japanese navy escorted the raiding
force sent against Pearl Harbor, and
gained air superiority over Malaya, the
Philippines and Burma. In the spring of
1942 the A6M3 with two-stage supercharged
Sakae 21 entered service, later
aircraft having their folding wing
tips removed. The Battle of Midway
represented the Zero's combat zenith;
thereafter the agile Japanese fighter
found itself ever more outclassed by
the American F6F Hellcat and P-38
Lightning. To counter the new American
fighters the A6M5 was rushed to
front-line units; this version, with Sakae
21 engine and improved exhaust system,
possessed a top speed of 565km/h, more A6M5s (and subvariants)
being produced than any
other Japanese aircraft. It was five
A6M5s of the Shikishima kamikaze unit
that sank the carrier St Lo and damaged
three others on 25 October 1944.
Other versions were the A6M6 with
water-methanol boosted Sakae 31 engine
and the A6M7 fighter/dive-bomber.
Total production of all A6Ms
was 10,937. (The reporting name'Zeke'
was given to the A6M, and 'Rufe' to a
float version, the A6M2-N.)
| MODEL | A6M2 |
| CREW | 1 |
| ENGINE | 1 x Nakajima NK1F "Sakae 12", 705kW |
| WEIGHTS |
| Take-off weight | 2410-2796 kg | 5313 - 6164 lb |
| Empty weight | 1680 kg | 3704 lb |
| DIMENSIONS |
| Wingspan | 12.0 m | 39 ft 4 in |
| Length | 9.06 m | 30 ft 9 in |
| Height | 3.05 m | 10 ft 0 in |
| Wing area | 22.44 m2 | 241.54 sq ft |
| PERFORMANCE |
| Max. speed | 525 km/h | 326 mph |
| Cruise speed | 330 km/h | 205 mph |
| Ceiling | 10000 m | 32800 ft |
| Range w/max.fuel | 3050 km | 1895 miles |
| Range w/max payload | 1850 km | 1150 miles |
| ARMAMENT | 2 x 20mm cannons, 2 x 7.7mm machine-guns, 60kg of bombs |
 | A three-view drawing (752 x 1009) |
| Ron, e-mail, 18.03.2012 06:27 Recently I came across the fact that the US testing of the first captured A6M2 was not flown in over-boost while the Japanese did use over-boost in combat against US fighters. Their pilots could get 345-348 mph out of it while US tests only went 331mph at best! Now I know why. Over-boost!
Perhaps that explains wide discrepancies in published initial climb rate as well. The US tests were 3100 fpm or less, but I've seen 4517 fpm elsewhere.
I used to wonder why the US pilots who survived the Battle of Wake Is, for example, would be not only out-turned but out-climbed and even out-run by A6M2 pilots although their USN F4F-3 could climb 3300 fpm and go around 330 mph. Yet they would complain about how out-classed they were in speed and climb as well as turn. Fantastic performance like 5000 fpm climb and unrealistic speeds were claimed for the Zero by the USN pilots. US Army P-39 and P-40 pilots too (from various battles)... and they could go over 331 mph. Go figure!
Before, I would think it was the quick acceleration of the A6M2 that explained the false impression of maximum speed and fpm initial climb rate. True, acceleration was a big advantage for the Japanese. But over-boost performance in the hands of Japanese pilots puts it all in a new light for me now. reply | | MARINER, e-mail, 29.01.2012 02:45 JAPANESES, HOJE MATAR BALEIAS INOCENTES E AINDA FICAR COM LUCRO. VIVA A AMERICA reply | | ARNOLD ANDERSON, e-mail, 29.09.2011 03:46 There is a lot of wild conjecture which is totally incorrect. To understand the origin of the Mitsubishi 0 obtain book, Eagles of Mitsubishi by, Jiro Horikoshi.
The author was lead designer of the airplane. reply | | Ron, e-mail, 28.02.2011 00:44 I found this:
"Considering the contemporary service aircraft were biplanes, Hughes fully expected the United States Army Air Forces to embrace his aircraft's new design and make the H-1 the basis for a new generation of U.S. fighter aircraft. His efforts to "sell" the design were unsuccessful. In postwar testimony before the Senate, Hughes indicated that resistance to the innovative design was the basis for the USAAF rejection of the H-1: "I tried to sell that airplane to the Army but they turned it down because at that time the Army did not think a cantilever monoplane was proper for a pursuit ship..."[7]
Aviation historians have posited that the H-1 Racer may have inspired later radial engine fighters such as the P-47 Thunderbolt and the Focke-Wulf Fw 190.[8] After the war, Hughes further claimed that "it was quite apparent to everyone that the Japanese Zero fighter had been copied from the Hughes H-1 Racer." He noted both the wing planform, the tail empennage design and the general similarity of the Zero and his racer.[9][N 2] Jiro Horikoshi, designer of the Mitsubishi Zero strongly refuted the allegation of the Hughes H-1 influencing the design of the Japanese fighter aircraft."
Lynn seems to take Hughes' verbose posturing concerning the Zero as fact.
Even a rudimentary comparison of the A6M Zero to his H-1 racer shows no such copying took place.
Historians see it inspiring possibly the P-47 or maybe the German Fw 190 but they don't include the Zero even if Hughes does.
Further, being inspired by a pre-war racer is not the same as buying it and copying it as a fighter plane.
His point that the US Army mentality was slow to accept the monoplane fighter concept like his H-1 was to prove true. But all fighter designers of WW 2 followed this path generally speaking.
Hughes' postwar hyperbole to stress his point was pandering to the war propaganda against Japan and the A6M Zero.
And certainly it deserved a challenge then and even more so now.
What are your thoughts? reply |
|
| | Ron, e-mail, 18.01.2011 06:55 D Lynn,
Do you have any credible evidence or proof.
Such a post is hard to take seriously otherwise.
Perhaps a half-truth maybe. Maybe not.
It begs for some light of day.
There was a time when such would pass for fact without further rigor, but that was in 1941 or 42! reply | | D Lyn, e-mail, 04.01.2011 21:36 I have heard that Howard Hughes designed the Zero and offered it to the U S but they wern't interested. It was made of spruce Plywood. The Japanese later bought it. reply | | Bill Brickhouse, e-mail, 02.01.2011 04:35 Looks like the ZERO has been cut short here. The A6M series started with the Model 11 and went thru the Model 63. Showing only the Model 21 is hardly telling the story of the A6M, I realize you cant show every detail but there is a lot missing. reply | | Ron, e-mail, 29.11.2010 23:09 For all the inexperienced pilots in the new A6M5, I'm amazed that only a couple of fighters did any better than it did to the end. reply | | Aaron, e-mail, 21.09.2010 18:39 Confidental report titled COMPARATIVE PERFORMANCE AND CHARACTERISTICS REPRESENTATIVE ENEMY AND ALLIED AIRCRAFT lists the ZEKE 32 and ZEKE 52 along with seven other Japanese fighters. The following are characteristics of the A6M2 type 32 ZERO: ZEKE 32 type 0, Mitsubishi /Nakajima.
Engine: Nakajima Sakae 12. 1120hp /S.L. 930hp /16,600ft. Armament: 2x20mm + 2x7.7mm. Range: 1,585mls /184mph /228gallons of fuel. Climb: 3580fpm /S.L. 2940fpm /18,600ft. 10,000ft /2.7min. 20,000ft /6.1min. This would make maximum climb rate around 3800fpm /5000ft. Maximum Speed: 297mph /S.L. 348mph /20,600ft.
The following is for the A6M5 type 52 ZERO: ZEKE 52 type 0, Mitsubishi: Engine: Nakajima Sakae 21. 1115hp /S.L. 965hp /19,700ft. Armament: 2x20mm + 2x7.7mm. Range: 1640mls /147mph /243gallons of fuel. Climb: 2800fpm /S.L. 2470fpm /19,700ft. 10,000ft /3.4min. 20,000ft /7.4min. Maximum Speed: 289mph /S.L. 354mph /21,000ft. Service Ceilings are listed as: ZEKE 32 - 35,900ft. and ZEKE 52 - 39,300ft.
Test weights were ZEKE 32 - 5650lbs and ZEKE 52 - 5920lbs. reply | | Ron, e-mail, 20.09.2010 07:33 Put another way, if the J2M had worked out when planned without the delays or the N1K had a BMW like reliable power plant, they could have replaced the Zero sooner on the production lines to better match the production of the new US Navy fighters. Meantime the Army's Ki 61 Tony was doing it's part (aside from the engine trouble). reply | | Ron, e-mail, 20.09.2010 07:03 D.Jay,
Even though some Zeros dove up to 460 mph from the later A6M5 models through the A6M6, and 7; but most A6M5 Zeros (the prolific initial lighter model before the A6M5a, b, and c) were only able to dive to 410 mph! So I presume your post is about the early war Zeros like the Model 11, 21, 22, and 32, which is true.
My post was obviously fanciful. It's interesting to wonder if the Japanese could have influenced each other a bit more (like the Allies), the Germans wouldn't have a 3+ second gap in turn vs Yaks and the Japanese wouldn't have suffered such a turkey shoot over the Marianas with slightly tougher, faster Zeros. reply | | D.Jay, 12.09.2010 18:09 Ron the Zero with MG 151 cannon an armoured seat and a BMW engine would not have worked,it was so manouverable because it was made with a light and feabel airframe. To take these mods it would have to have been strengthend so much it would then be heavy so turn rate would have not been so inpresive. also it was unflyable at speeds over 380mph (in a dive) and at over 400 the wings would come off. It was no Spitfire, where the Spitfire could take bigger engines and bigger guns with out much trouble the zero had no room for improvments. reply | | Francis Dec, e-mail, 04.08.2010 07:11 Did Japan ever sell export versions of their aircraft? Imagine Poland buying A5M's and using them in 1939? reply | | Ron, e-mail, 08.08.2010 05:36 In 1940 if the Luftwaffe got an A6M2 Model-11, Can you imagine the range and turn rate German planes would incorporate afterward. Maybe they would return it back to Japan later on with 2 or 4 fast MG 151 cannon and an armored seat not to mention a boosted BMW radial engine! reply | |
| | Ron, e-mail, 03.06.2010 06:34 Dude,
Sorry the Zero makes you feel that way. Take a look see at the Mitsubishi J2M5 Raiden. The RAF was impressed.
Want quantity? Try the Nakajima Ki 84 Hayate. The US took notice.
The one that impressed the Japanese themselves was the Kawasaki Ki 100 Goshikisen!
Of course the A6M2 Zero was king in 1942. Unfortunately it was forced to stay in the ring well past it's prime. This kept the major production effort away from those newer contenders. So, Japan suffered. Thus you have reason to like the Zero. Think about it Dude. reply | | Ian, e-mail, 28.05.2010 11:49 I wish to build a 75% flying aircraft ( light sports aircraft) can anyone help with construction plans please reply | | Ta-183 Huckebein, 16.05.2010 16:04 That airplane starred in 'Tora, Tora, Tora!', 'Pearl Harbor', and 'The Countdown' reply | | Mike Dunne, e-mail, 18.03.2010 07:36 The very knowlegable Captain Eric Brown RN test flew just about every plane used in WWII including even the Me 163. He was a great admirer of the Zero. He tested them quite extensively and declared (and still does to this day) that the Zero was the best FIGHTER of the war up till mid 1943!
Forget outright speed! When the air fight starts, everyone is doing around 300mph max! If you haven't been in a sky full of hotheads hurtling about trying to kill one another, you really don't get the picture! The Zero was doing its best work at this speed...throttle right open and FIGHT! Same goes for the Hellcat... reply | | Ron, e-mail, 03.09.2010 22:52 Francis, Japan did get a Bf 109 and an Fw 190 from Germany.
I haven't heard of the reverse. reply | | Leo Rudnicki, 29.11.2009 11:13 Thank you for the correction on 20 mm cannons. Regarding radios, all Zeroes were originally fitted with radios and radio direction finders. All shipboard Zeroes carried radios for RDF. Unit commanders had a code key for reporting. However, voice comm was not possible using the set since installation and static suppression had never de-bugged due to lack of coordination between a /c, engine and radio manufacturers. Hence the use of flares at Pearl Harbour. Hence the mention by Saburo Sakai that he regretted not being able to warn fellow pilots that they were being bounced. Land-based Zeroes commonly removed the sets completely to save weight since RDF was not a factor. reply |
|
Do you have any comments?
|
| 
COMPANY
PROFILE
All the World's Rotorcraft
|









20
reply