 |
Dassault-Breguet / Dornier Alpha Jet1973 |  |
| TRAINING, CLOSE-SUPPORT AIRCRAFT | Virtual Aircraft Museum / Joint Projects / Dassault-Breguet/Dornier |
 |
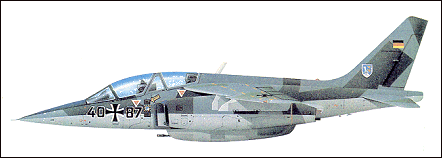
One of a number of international aircraft development and production programmes that have been initiated since the end of World War II, the Dassault-Breguet/Dornier Alpha Jet was announced as a design and development programme on 22 July 1969. Both France and West Germany required a new subsonic basic/advanced trainer and light-attack aircraft to replace in-service Lockheed T-33A, Fouga Magister and Dassault Mystere IVA trainers and Aeritalia (Fiat) G91 attack aircraft. Following a design submission by Dassault-Breguet and Dornier to meet this requirement, it was announced on 24 July 1970 that the Alpha Jet had been selected and French and West German government approval for a start to the programme was given in late 1972. Following evaluation of prototypes the go-ahead for production in quantity was given on 26 March 1975. A cantilever shoulder-wing monoplane of all-metal construction, the Alpha Jet has a swept wing and tail surfaces, retractable tricycle landing gear, accommodation for two persons in tandem seated on ejection seats, and powerplant comprising two SNECMA/Turbomeca Larzac turbofan engines. It is available in basically four versions: the Alpha Jet E(Ecole) advanced trainer for France; the Alpha Jet A(Appui) light-ground attack aircraft for Germany; the Alpha Jet 2, originally known as the MS-1 and MS-2 versions and latterly the NGEA (Nouvelle Generation d'Ecole et d'Ataque) incorporating new avionics, a head-up display, inertial navigation system and a laser rangefinder to provide optimum weapon delivery capability, and lastly, the Alpha Jet 3 ATS (Advanced Training System/Advanced Tactical Support) originally launched in the mid-1980s as the Lancier. The Alpha Jet 2 has a fully integrated SAGEM Uliss 81 INS, TRT radar altimeter, SFIM gyro-magnetic compass, Thomson-CSF HUD and a TMV 630 laser/rangefinder mounted in the nose. More powerful Larzac 04-C20 engines delivering 1440kg thrust each are also fitted. The Alpha Jet 2 first flew in April 1982 and delivery was made to Egypt (which ordered 45) in June 1983 with seven following for the Cameroon. Evolved from the Alpha Jet 2, the Larzac 04-C20 powered Alpha Jet 3 ATS is effectively a flying simulator equipped to lead pilots into new advanced combat aircraft such as the Mirage 2000, Rafale, Gripen and F-16 and other types expected to enter service between 1990-2010. The ATS is equipped with an advanced VEM 130 HUD, new types of sensors, day/night navigation and intercept radar such as Agave/Anemone, FLIR pod, a laser-designator pod, laser-guided stand-off weapons and electronic warfare systems. The first of four Alpha Jet prototypes made its maiden flight on 26 October 1973; delivery of the Alpha Jet E for the French Armee de I'Air began during the summer of 1978 and of the Alpha Jet A for the Federal German Luftwaffe in March 1979. The requirements of these two services, 200 and 176 respectively, were completed in early 1982 and orders for all versions of the Alpha Jet have reached just over the 500 mark. They include, in addition to the French and German requirements, examples for Belgium (33), Egypt (45), Ivory Coast (7), Morocco (24), Nigeria (24), Qatar (6), Cameroon (7) and Togo (5). One Alpha Jet A was modified during 1980 to evaluate an experimental transonic wing of super-critical section which has been developed by Dornier. Other changes to this aircraft, first flown in its new form on 12 December 1980, include the incorporation of leading- and trailing-edge manoeuvring flaps.
|  All the World's Rotorcraft | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |

|
