|
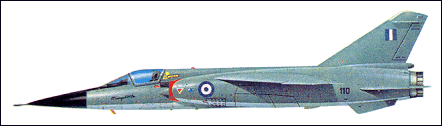
| Evolved in parallel with the Mirage F2 as a scale-down,
multi-role single-seat fighter employing a
SNECMA Atar turbojet, the Mirage F1 was conceived
as a successor to the Mirage IIIC and was the subject of
a government contract awarded in 1964. Possessing,
like the F2, a conventional sweptback wing generously
equipped with high-lift devices, and conventional
swept tail surfaces, the private venture prototype F1
flew on 23 December 1966. Three pre-series aircraft
were ordered in September 1967, the first of these flying
on 20 March 1969. The initial production model for
France's Armee de l'Air was designated F1C, placed
emphasis on the intercept mission, was powered by an
Atar 9K-50 turbojet affording 7200kg
with afterburning, and had an armament of two 30mm
cannon, two Matra 550 Magic and two Matra R 530 or
Super 530 AAMs. An initial order for the F1C for the
Armee de l'Air was placed in 1969, 162 being procured
by that service (plus 64 recce F1CRs and 20 two-seat
F1B trainers), initial operational capability being
achieved in 1974. Many of the Armee de l'Air aircraft
were delivered in, or retroactively modified to, F1C-200
standard with a 8cm fuselage plug to accommodate
a removable flight refuelling probe. Variants of
the basic aircraft offered for export, in addition to the
F1C, were the F1A with simplified avionics for operation
under VFR conditions and the F1E multi-role air
superiority/ground attack/reconnaissance version. Export customers were Ecuador (16 F1AJs), Greece (40
F1CGs), Iraq (113 F1EQs), Jordan (17 F1CJs and 17
F1EJs), Kuwait (27 F1CKS), Libya (16 F1ADs and 16
F1EDs), Morocco (30 F1CHs and 20 F1EHs), Qatar (12
F1EDAs), South Africa (32 F1AZs and 16 F1CZs) and
Spain (45 F1CEs and 22 F1EEs). Production of the Mirage
F1 was completed in 1990 with 731 built (including
F1B and F1D two-seat trainers and F1CR reconnaissance
aircraft). In 1991, work began on the adaptation of
30 F1C-200S as F1CT ground attack fighters.
 | A three-view drawing (1653 x 1330) |
| MODEL | Mirage F1C |
| ENGINE | 1 x SNECMA Atar 9K-50, 7200kg of reheat thrust |
| WEIGHTS |
| Take-off weight | 15200 kg | 33510 lb |
| Empty weight | 7400 kg | 16314 lb |
| DIMENSIONS |
| Wingspan | 8.4 m | 28 ft 7 in |
| Length | 15 m | 49 ft 3 in |
| Height | 4.5 m | 15 ft 9 in |
| Wing area | 25 m2 | 269.10 sq ft |
| PERFORMANCE |
| Max. speed | 2350 km/h | 1460 mph |
| Ceiling | 20000 m | 65600 ft |
| Range w/max payload | 900 km | 559 miles |
| ARMAMENT | 2 x 30mm cannon, 4000kg of weapons |
| jpj, e-mail, 01.10.2017 19:03 In response to Gulf War Boy, the french F1 could not fly over Irak as Irak also had these aircrafts and there was a major risk of friendly fire. France engaged some Jaguar which participated in various bombing missions. reply | | Gulf War boy, e-mail, 26.09.2017 11:16 Undoubtedly France shows its back stabbing nature by co-operating with other forces when it suits and then runs away when things get tough, as shown when a Squadron of Mirages were stationed at Al kharj when coalition forces were patrolling the no-fly zone over Iraq. Our aircraft would fly every day over Iraq and the French would fly every 7 and even then would turn back before getting to the Iraqi border. As soon as Op Telic came - guess what? The French disappeared in a cloud of dust. reply | | Paul Scott, 27.03.2015 16:09 Undoubtedly showing the French /Dassault's commitment to procuring excellent air designs, a pity the British government gave up on itself past 1960 in that respect after leading with America. reply | | Mathi, e-mail, 06.06.2011 10:53 Is Mirage F1CZ fighter used during the Gulf war?
Inform me in details. Thanks. reply | |
| | steve, e-mail, 02.06.2011 19:01 The F1 has always struck me as how the F-104 should have been - adequate wing area and the horizontal tail in the right place. reply | | FRANK, e-mail, 11.01.2011 21:52 The Mirage F1 served with distinction, particularly in the Greek Hellenic Air Force, where her arrival proved a deterrent to Turkish air space incursions for some 28 years. Over 720 Mirage F1 examples have been produced. The F1 remains one of the most battle-tested aircraft systems of the Cold WarThe F1 first flew in a Dassault-funded prototype form on December 23rd, 1966, intended as a replacement for the aging Mirage III and Mirage 5 models. Unlike previous Dassault offerings, the F1 did away with the traditional low-mounted, delta-wing configuration and instead was fitted with a high-mounted, swept wing arrangement. The French Air Force liked what it saw in the promising design and selected it for further development in the form of additional prototypes in May of 1967. reply | | SONDY, e-mail, 11.01.2011 21:47 Mirage Initial and Recurrent TraininG reply | | HONY, e-mail, 11.01.2011 21:42 Another fine COMBOTE aircraft reply | | rager, e-mail, 11.01.2011 21:39 the war MISSION that F-1 WAS THERE reply | | mike, e-mail, 11.01.2011 21:30 show some new pictures with bombing mission reply | | pohang, e-mail, 31.12.2010 08:47 show some picture of this figther ability reply | | pohang, e-mail, 31.12.2010 08:47 show some picture of this figther ability reply | | dawod, e-mail, 25.12.2010 21:06 can mirage f-1 carry pl-7 missile without any change in designed wiring ? reply | | a.casais, e-mail, 02.12.2010 21:27 This beatiful plane was in Spain, the ala(squadron)-13, so called "no le pises los tres pies al gato" that means " do not step on the 3 cat foots" or some thing like that. Is the elite squadron, now is the "F-18 Hornets" who rules. reply | |
| | hamed, e-mail, 19.06.2010 19:29 The Dassault Mirage F1 series was designed to replace the successful Dassault Mirage III series. With a host of new features added to this new aircraft, the Mirage F1 would be a substantial upgrade to the whole Mirage family that would continue in service well into the new millennium. The Mirage F1 was built with capability and a multi-role perspective in mind. The aircraft was designed for high-speed handling with low or high-altitude performance, multi-faceted capabilities in the fighter or strike aircraft role and provide the pilot with some minor conveniences for long sorties requiring short turnaround times. The Mirage F1 served with distinction, particularly in the Greek Hellenic Air Force, where her arrival proved a deterrent to Turkish air space incursions for some 28 years. Over 720 Mirage F1 examples have been produced. The F1 remains one of the most battle-tested aircraft systems of the Cold WarThe F1 first flew in a Dassault-funded prototype form on December 23rd, 1966, intended as a replacement for the aging Mirage III and Mirage 5 models. Unlike previous Dassault offerings, the F1 did away with the traditional low-mounted, delta-wing configuration and instead was fitted with a high-mounted, swept wing arrangement. The French Air Force liked what it saw in the promising design and selected it for further development in the form of additional prototypes in May of 1967. The French Air Force envisioned the type as an all-weather interceptor capable of handling any of the new generation threats available. The resulting design proved a far better product than the aircraft the F1 was intended on replacing, sporting high-performance, sleek lines and a powerful Cyrano radar system. Production inevitably commenced and full operational status was achieved in May 1973.
The single engine, high-mounted swept-wing aircraft was powered by a single SNECMA Atar 9K-50 afterburning turbojet 15,785lb engine fed by two side-mounted intakes. The F1 sported a single-seat cockpit positioned in the forward portion of the streamlined fuselage. Amenities such as a self-starter, shaded canopy glass and pressured refueling system provided operators of the aircraft with the advantage of a low maintenance, highly capable aircraft. Further developments (beginning with the Mirage F1C-200) went on to integrate an in-flight refueling probe to which the combat radius was increased substantially. The unique high-mounted swept-wing design coupled with the single vertical tail fin afforded the aircraft the ability to take off and land with a minimal use of runway.
Standard armament were twin 30mm cannons along with 2 x Matra R530 series medium-range air-to-air missiles. Missiles were initially held under the wings though wingtip rails were later added for the use of Matra R550 Magic and AIM-9 Sidewinder short-range air-to-air missiles, the latter at the behest of the American-friendly Hellenic Air Force of Greece (operating Mirage F1CG models of their own).
The base F1 fighter was exported as the F1CE (Spain), F1CG (Greece), F1CH (Morocco), F1CJ (Jordan), F1CK (Kuwait), F1CK-2 (Kuwait - follow-up order) and F1CZ (South Africa) with orders totaling some 175 exported aircraft. The two-seat F1B trainer was marketed overseas as well along with the F1A single-seat ground-attack fighter. The F1E became an all-weather, multi-role fighter and ground-attack variant. The Mirage F1D was a two-seat trainer spawned from the F1E multi-role, ground-attack fighter model. The Mirage F1CR was a dedicated reconnaissance model. The Mirage F1CT became a tactical ground attack variant based on the Mirage F1C-200. F1AZ and F1CZ were South African exports of ground-attack and radar-equipped models respectively. The Mirage F1CG were Greek-operated single-seat fighters, amounting over 100,000 thousand hours of flight time over water with little structural stress to show for it. The Mirage F1M-53 was a developmental Mirage F1 meant to compete in NATO trials for replacing the Lockheed F-104 Starfighters then in service (the General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon eventually won out).
The aircraft became a highly regarded interceptor - one of the best at the time of its inception - based on capabilities and its powerful nose-mounted radar. The system could track and engage multiple targets at any altitude all at the discretion of the pilot. The integrated weapon system could go so far as to select the appropriate weapon based on circumstance and fire the weapon when the target achieved an in optimal range.
In terms of combat exposure (the sure testing grounds of any aircraft design) the F1 was at the fore-front of several Cold War-era conflicts the world over. Mirages participated with the South African Air Force in their Border War. Morocco utilized the type to combat local rebels. Ecuador fielded the aircraft in their Paquisha War and follow-up Cenepa War against Peru. France got a chance to check out the F1's lethality in its actions against Li ... reply | | hamed, e-mail, 19.06.2010 19:26 many of kuwaiti mirage's was is in iraq in gulf war 2 and american has distroyer them reply | | hamed, e-mail, 19.06.2010 19:21 The iraqi mirage is in service with iran in mashhad airport in squadron 140 reply | | JT, e-mail, 27.01.2010 06:03 Have a Qnty of 27 , Mirage 1's for Sale.. only Serious Buyers.
Must have a Valid EUC reply | | paul scott, e-mail, 17.08.2009 18:19 Another fine aircraft from Dassault. reply |
|
Do you have any comments?
|
| 
COMPANY
PROFILE
All the World's Rotorcraft
|








